在 .NET 开发中,表达式树是一个强大但容易被忽视的特性。如果你使用过 Entity Framework 或 LINQ to SQL,其实你已经在间接使用表达式树了。
什么是表达式树?
表达式树(Expression Tree) 是用树形数据结构来表示代码逻辑运算的技术,它让我们可以在运行时访问逻辑运算结构。表达式树在.net中对应Expression<TDelegate>类型。
通俗理解
- 普通委托:是一段可执行的代码
- 表达式树:是描述代码结构的数据,可以被分析、修改、翻译成其他形式(如 SQL)
一个简单的例子
1 | // 普通委托:直接执行 |
为什么需要表达式树?
表达式树的主要用途是将 C# 代码翻译成其他形式:
- LINQ to SQL / Entity Framework:将 C# 查询翻译成 SQL 语句
- 动态查询构建:根据用户输入动态生成查询条件
- 代码分析:检查代码结构、提取元数据
- 序列化/反序列化:将代码逻辑保存或传输
Expression 和 Func 的区别
Func<T> - 委托
Func<T> 是一个委托类型,代表可执行的代码。
1 | Func<int, int, int> add = (a, b) => a + b; |
特点:
- 编译后直接生成 IL 代码
- 可以直接调用执行
- 无法查看内部结构
Expression<Func<T>> - 表达式树
Expression<Func<T>> 是一个表达式树类型,代表代码的数据结构。
1 | Expression<Func<int, int, int>> addExpr = (a, b) => a + b; |
特点:
- 编译后生成表达式树对象(包含 Body、Parameters 等属性)
- 不能直接调用,需要先编译成委托
- 可以分析、修改、翻译
对比表格
| 维度 | Func |
Expression<Func |
|---|---|---|
| 本质 | 委托(可执行代码) | 表达式树(代码的数据结构) |
| 是否可执行 | ✅ 直接执行 | ❌ 需要先编译成委托 |
| 是否可分析 | ❌ 无法查看内部结构 | ✅ 可以访问树形结构 |
| 典型用途 | LINQ to Objects、回调函数 | LINQ to SQL、动态查询 |
实际应用场景对比
1 | // LINQ to Objects:使用 Func(在内存中执行) |
总结
Expression类似于源代码,Func类似编译后的二进制程序。
查看表达式树的结构
表达式树是一个树形结构,可以通过其属性查看内部组成。
Visual Studio通过自动窗口查看
1 | Expression<Func<int, bool>> expr = x => x > 5; |
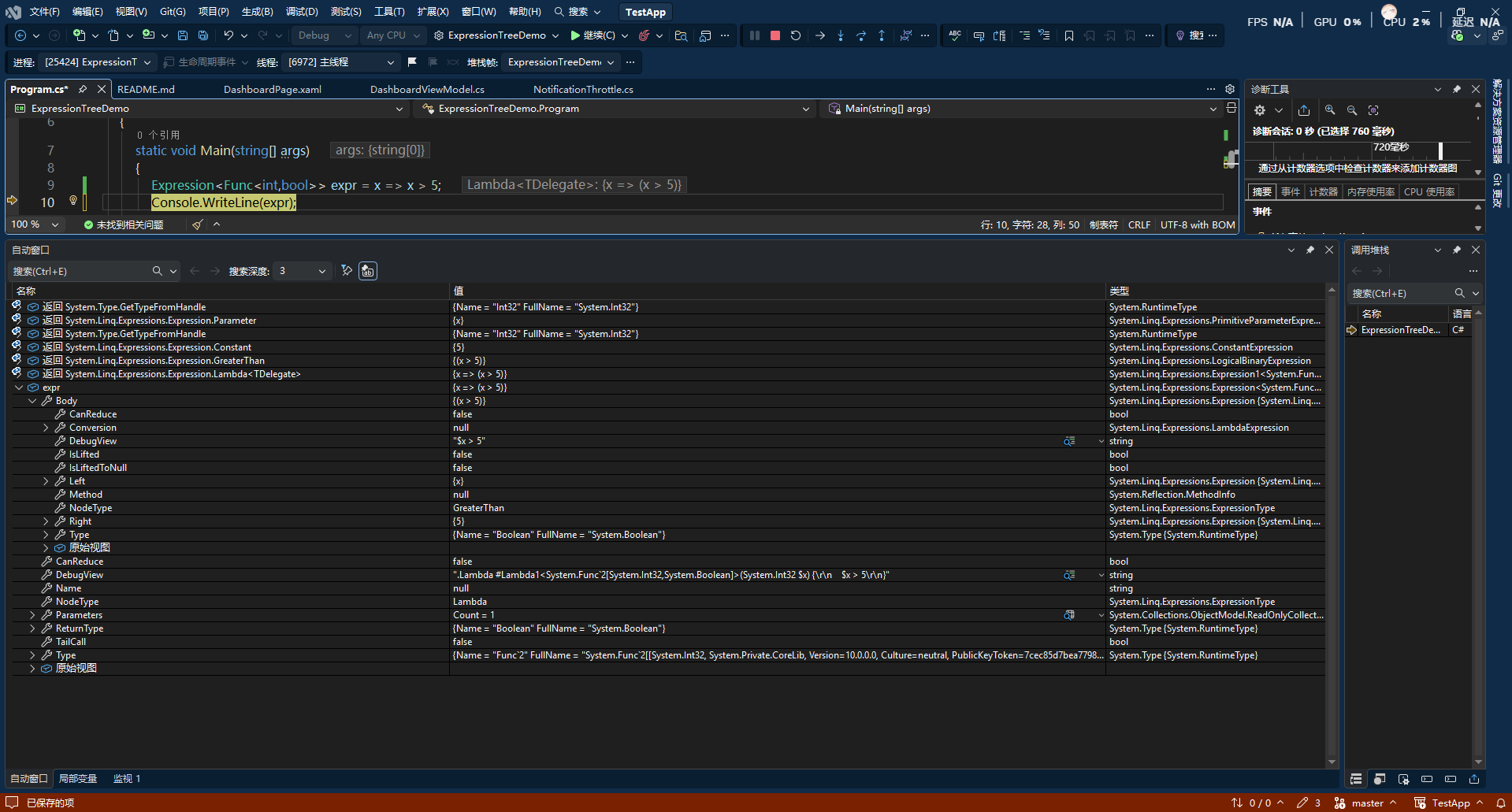
可以看到expr NodeType是Lambda,Body下面有Left {x}和Right {5} ,Body的 NodeType 是 GreaterThan,它是 二元运算符节点类型 BinaryExpression ,GreaterThan表示大于
代码查看表达式树
使用包ExpressionTreeToString
1 | Expression<Func<int,bool>> expr = x => x > 5; |
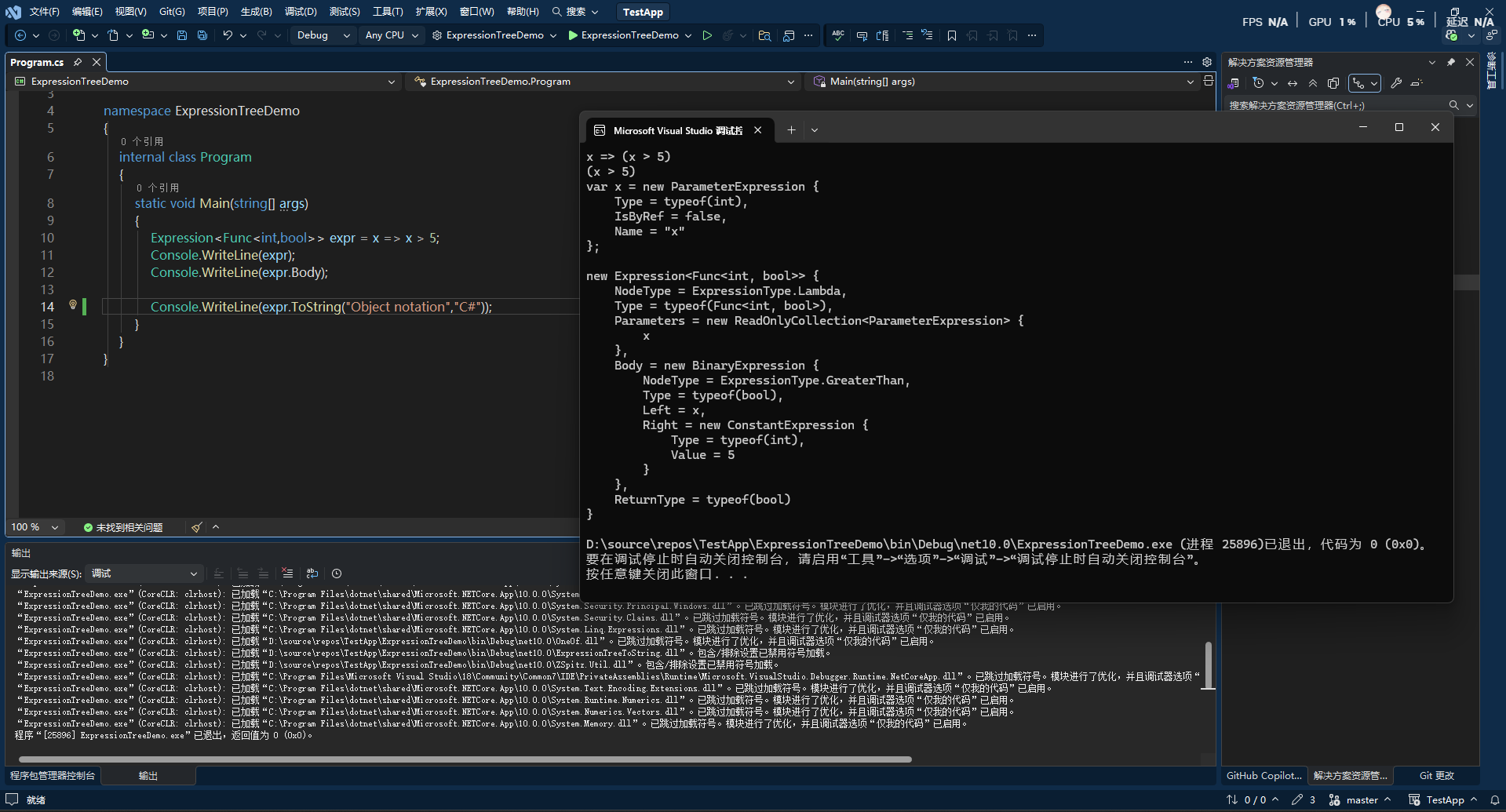
可以看到,表达式树不同类型的节点对应不同类型,这些类型直接间接继承Expression。如上面Body就是二元运算符节点类型 BinaryExpression、Lambda 表达式 LambdaExpression(如 x => x > 10)、方法调用 MethodCallExpression(如 obj.ToString())、成员访问 MemberExpression (如 obj.Name、x.Age)、常量 ConstantExpression 、参数 ParameterExpression。
而NodeType表示标识当前表达式节点的类型,是ExpressionType枚举值。
1 |
|
递归遍历表达式树
1 | using System.Linq.Expressions; |
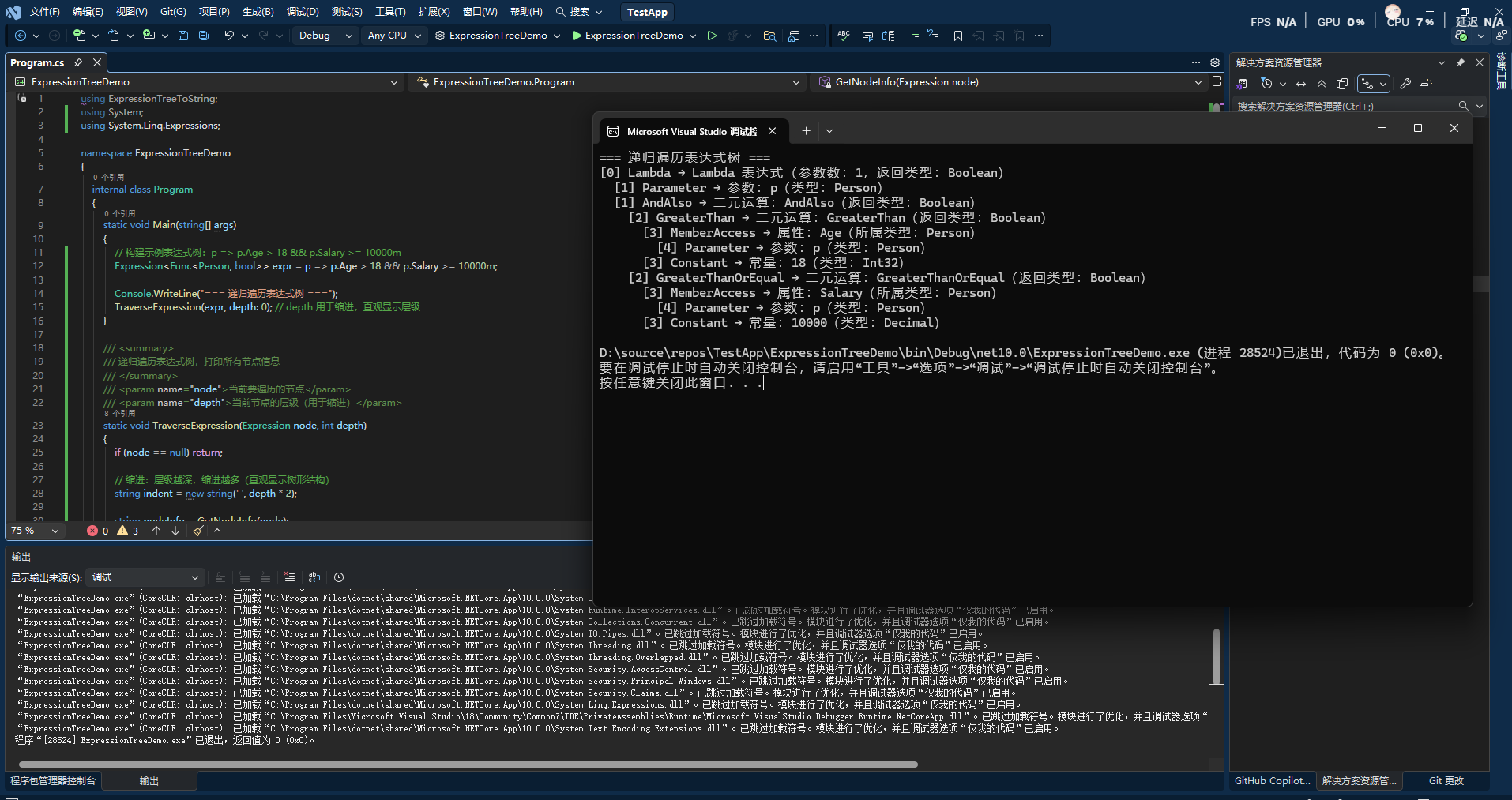
总结
| 概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 表达式树 | 代码的树形数据结构,可以被分析和翻译 |
| Func |
可执行的委托,用于 LINQ to Objects |
| Expression<Func |
表达式树,用于 LINQ to SQL/EF |
关键要点
- 表达式树是”代码的数据”,不是”可执行代码”
Expression<Func<T>>可以被翻译成 SQL 或其他语言- 手动构建表达式树适用于动态场景,但不要过度使用
- 优先使用 Lambda 表达式,保持代码简洁